GUM DISEASE
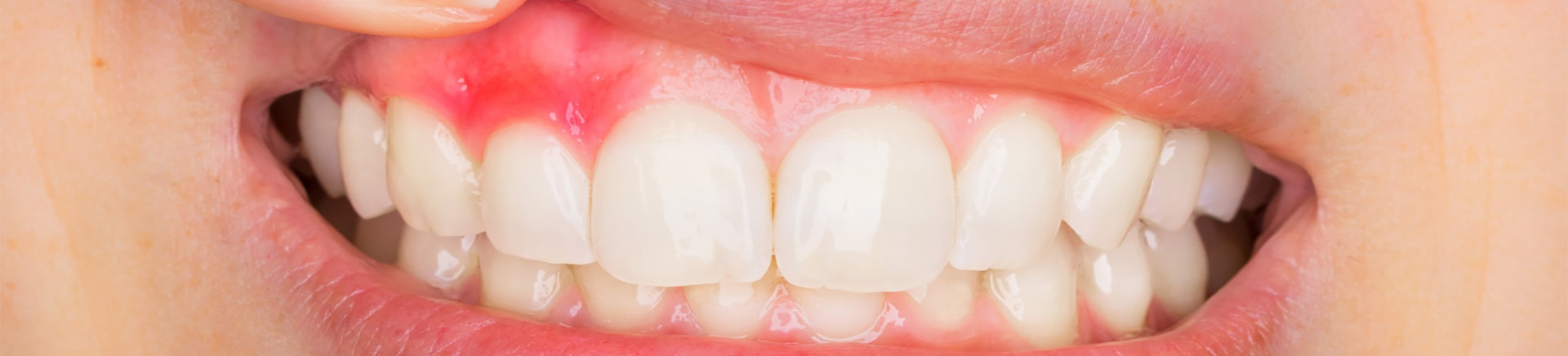
Is spitting blood during brushing normal?
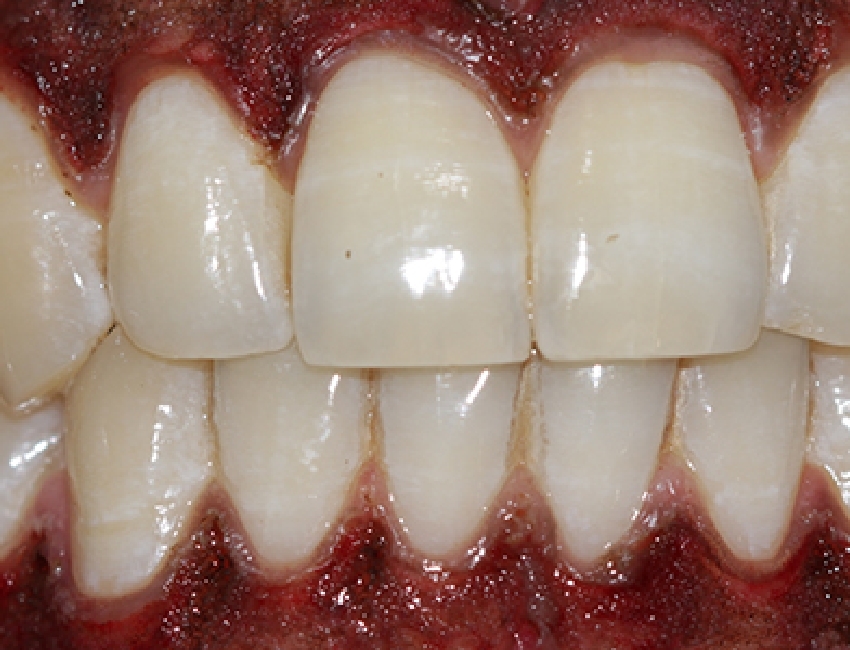
Are healthy gums supposed to bleed?
Is it ok if my gums look red?
The answer to all the above questions is NO.
Healthy gums don’t bleed. Healthy gums are neither swollen nor reddish.
It is important for you to visit the dentist if you are experiencing any of the above symptoms.
Bleeding swollen gums are the first sign of underlying gum disease.
If not treated on time it will progress to ‘Periodontists’
Gum disease also known as ‘Gingivitis’ is a serious infection of gums which weakens the supporting structure of the tooth.
If left untreated, gum disease progresses into ‘Periodontitits’
Periodontitis is a grave infection of the gums and the underlying bone structure. The bone surrounding the root of the tooth is the one which supports the tooth. When this gets affected, the disease eats away at the bone.
Signs of gum disease
- Bleeding gums
- Swollen gums
- Pus in gums
- Bad breath
- Mobile teeth
1. Is gingivitis reversible?
If proper treatment is taken at the right time, the early stage of gingivitis is reversible. Timely treatment is the key to healthy gums.
2. What are signs of gingivitis?
- Swollen gums
- Bleeding gums
- Pus in gums
- Bad breath
- Tender gums
3. What are signs of periodontists?
- Pockets around teeth
- Bad breath
- Mobile teeth
- Tender teeth and gums
4. How can gingivitis be prevented?
Gingivitis is totally preventable if you follow the following
- Brush twice daily using fluoridated toothpaste and soft bristled toothbrush
- Gargle and rinse after every meal
- Floss twice daily
- Visit the dentist every 6 months for a routine check up.
- Get professional teeth cleaning done every 6 months and/or whenever advised by the dentist.
- Teeth cleaning / Scaling – Tartar and calculus deposits are removed so as to remove the irritant
- Root planing – Removal of calculus is done from the root surfaces of roots
- Antibiotics – Adjunctive to scaling, antibiotics are also prescribed to reduce the infection
- Flap surgery – Gum tissue is folded back to remove the tartar and calculus deposits present on deep surfaces of teeth and roots
- Soft tissue grafts – A piece of soft tissue is transplanted to cover the defect left due to periodontitis
- Bone graft – Once the infection is cleared out, the bone defect can be treated with bone graft so as to restabilize the tooth.
The treatment for gum diseases depends on the severity of the disease and the charges differ accordingly.
Ranges from NPR 3000 to NPR 20000
BOOK AN APPOINTMENT